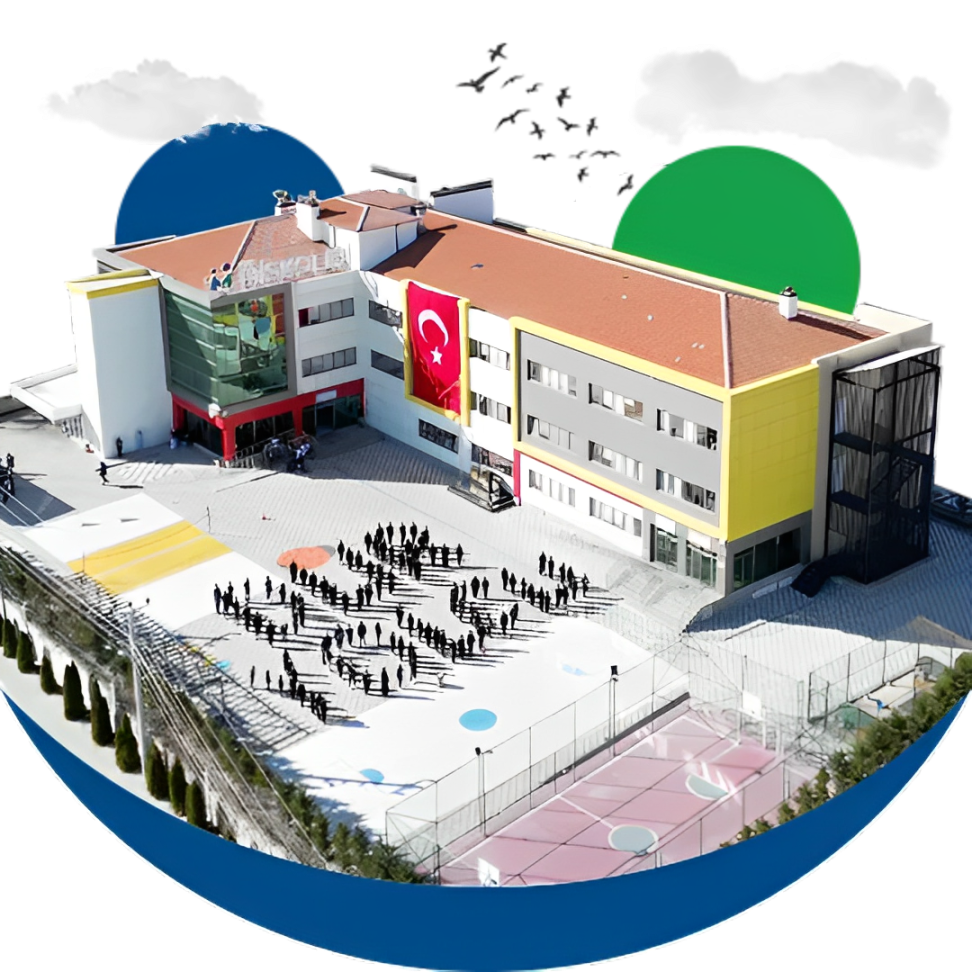
Kurumsal
Sevgili Öğrencilerimiz,
Değerli Velilerimiz ve Kıymetli Eğitimcilerimiz,
Eğitim, bir toplumun en büyük gücüdür. Mis Koleji olarak bizler, sadece akademik başarıyı değil, ahlaki değerleri, bireysel gelişimi ve evrensel düşünmeyi de temel alan bir eğitim anlayışını benimsiyoruz.
Mis Koleji Yönetim Kurulu Başkanı
Salih ÖZKAN


EĞİTİM PROGRAMI
+
ÖĞRENCİ
+
EĞİTİM KADROMUZ
Misden Eğitimlerimiz
Akademik Eğitim
Akademik Eğitimde Mis Koleji Farkı
Mis Koleji, geleceğin liderlerini ve bilim insanlarını yetiştirme misyonuyla öğrencilerine çağdaş, bilimsel ve tekno...
Yabancı Dil Eğitimi
Yabancı Dil Eğitiminde Mis Koleji Farkı
Mis Koleji olarak, öğrencilerimizin küresel dünyada başarılı olabilmesi için dil becerilerini geliştir...
Değerler Eğitimi
Mis Koleji Değerler Eğitimi ile Geleceğin Sorun Çözebilen Bireyleri Yetiştiriyoruz
Mis Koleji olarak, öğrencilerimizin sadece akademik alanda değil, ...
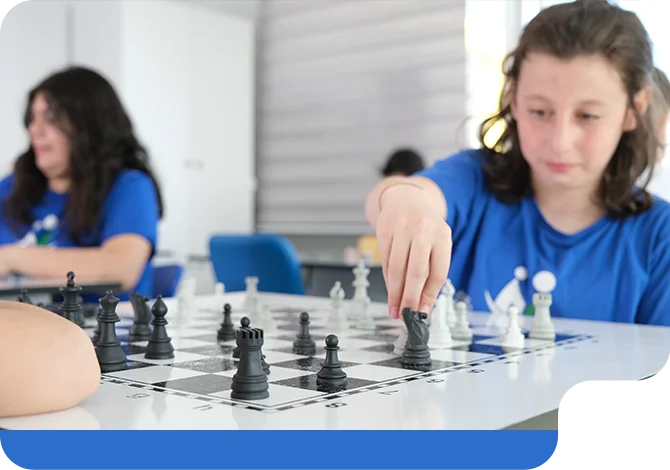

Misden Etkinliklerimiz
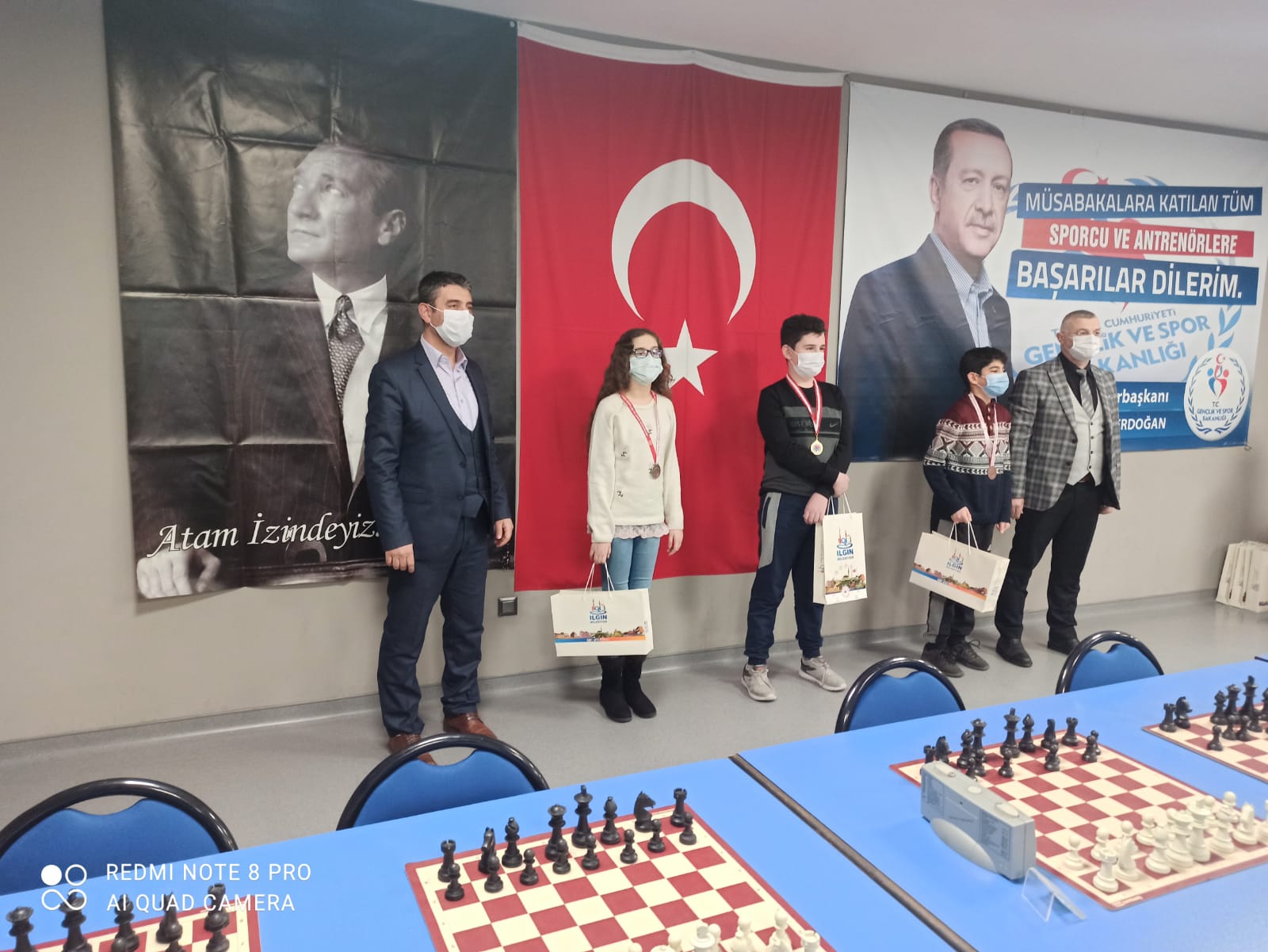
Öğrencilerimizin bilimsel ve analitik düşünme becerilerini geliştiren proje ve yarışmalar düzenliyoruz.
Resim, müzik, tiyatro ve dans etkinlikleriyle öğrencilerimizin yaratıcılığını destekliyoruz.
Takım ruhunu güçlendiren spor turnuvaları ve doğa gezileri düzenliyoruz.

Mis Store
Mis Storeda, okulun kıyafetleri ve giyim kuralları hakkında bilgilere ulaşabilirsiniz..
Mis Store
Eğitmen Girişi Yap
Eğitmen girişi yaparak, eğitmen olarak yazılar oluşturabilir ve içeriklerinizi paylaşabilirsiniz.
Eğitmen GirişiEğitmenden Yazılarımız
Eğitmenlerimizin eğitim, rehberlik ve gelişime dair paylaşımlarını keşfedin.
Tümünü İncele
Matematikte başarılı olmak, disiplinli bir çalışma ve doğru yaklaşımlar gerektiri...
Yazıyı İnceleAli ATABEK
Matematik ÖğretmeniHaberlerimiz
Mis Koleji yeni eğitim öğretim yılına hazır
Mis Kolejinde Bahar Şenliği Coşkusu Başladı
...- Mis Koleji